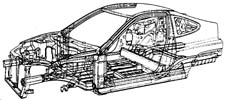
In city driving, much of a vehicle's power is consumed accelerating and decelerating. A lighter vehicle requires less energy to accomplish this, so Honda engineers specified aluminum alloy as the material of choice for the Insight. With the exception of its plastic front fenders, rear fender skirt and trim pieces, all of the Insight's major body panels are made from this lightweight alloy. As a result, the Insight body is 40 percent lighter than a comparable steel body, such as the Civic Hatchback, yet it possesses 13 percent greater bending rigidity and 38 percent more torsional rigidity.
From their experience building the Acura NSX - the world's most produced aluminum-bodied car - Honda engineers have gained extensive knowledge of aluminum. However, the Insight is designed for a very different purpose.
Market requirements dictated the development of new, more cost-effective techniques for manufacturing the Insight's aluminum body. In response to this challenge, Honda engineers developed the Insight's innovative unit-body/space-frame construction.
The unit-body part of the Insight's body uses stressed sheet-metal panels to absorb and distribute structural and suspension loads, much like an ordinary steel unit body. However, with the Insight's body all of these panels, including the roof, floor, front and rear wheelwells, rear quarter-panels, bulkhead, and even the doors and hood, are made of aluminum alloy. These stressed panels are reinforced in key areas by aluminum-alloy frame members.

It is these aluminum frame members and their cast-aluminum connecting joints that make the Insight's hybrid body so unique. In a steel unit body, frame members are formed by stamping in large presses and then joined to the body by welding. However, the Insight uses extruded frame members. Extrusions are drawn from a die in much the same way that tubing is made, and like tubing are of constant cross section. Once formed, extrusions can be easily made into complex three-dimensional pieces, such as a curved windshield frame. They also do not require any additional machining or finishing after they are formed.
On the Insight, each frame member's size and strength is optimized so that the frame is strong where it needs to be, and lighter in less critical areas. A variety of shapes are used, including hexagons, ovals, H-sections and reinforced box-sections. The door and windshield pillars, front and rear side-frame members, lower body sills, crossmembers and floor frame members are all formed in this manner.
In more highly loaded areas of the body (such as the front and rear subframes), larger, internally ribbed, hexagonal aluminum frame members are used. These are joined to other frame members via rigid, die-cast aluminum joints. Die-castings are also used at engine and suspension mounting points. These die-castings offer versatility and cost savings, because they can be designed to suit specific size, space and strength requirements.